Near the surface of Earth, object with
weight can float in fluids. The fluid must exert a force on a floating
object equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the object's
weight. Where does this force come from?
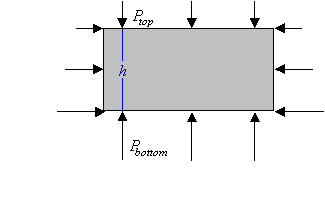 Consider again the box-shaped volume of
water in equilibrium at some depth in the pool. The upward force
provided by the surrounding water must exactly balance the force of
gravity acting on the water in the box. The upward force provided by
the surrounding water must be equal to the weight of water in the box.
Consider again the box-shaped volume of
water in equilibrium at some depth in the pool. The upward force
provided by the surrounding water must exactly balance the force of
gravity acting on the water in the box. The upward force provided by
the surrounding water must be equal to the weight of water in the box.
If we replace the volume of water with a box of the same shape
containing some other material, then the net upward force provided by
the surrounding water does not change. It depends only on the
difference in the pressure at the top and at the bottom of the box. But
the weight of the box changes, and therefore the net force on the box
changes. If the weight is greater than that of the corresponding volume
of water, the net force is downward and the box will accelerate downward
and fall. If the weight is less than that that of the
corresponding volume of water, the net force is upward and the box will
accelerate upward and rise.
This is Archimedes' principle. It holds for all fluids, i.e. it holds for all liquids and gases.
An object partially or wholly immersed in a gas
or liquid is acted upon by an upward buoyant force B equal to the weight
w of the gas or liquid it displaces.
B = w
External link: Buoyancy Brainteasers
Problem:
A 2 kg block of wood is floating in water. What is the magnitude of the
buoyant force acting on the block?
Solution:
- Reasoning:
The block is floating, it is not accelerating, the net force must be zero.
So the magnitude of the buoyant force must be equal the weight.
- Details of the calculation:
B = mg = 19.6 N.
Problem:
The density of freshwater is 1 g/cm3 and the density
of seawater is 1.03 g/cm3. Will a ship float higher in
freshwater or seawater?
Solution:
- Reasoning:
When an object floats, the weight of the displaced water equals the weight
of the object. You need less of the denser seawater to make up the weight
of the ship than you need of the less dense fresh water. Therefore the ship
displaces less seawater and floats higher in seawater.
Problem:
A Styrofoam slab has a thickness h and a density ρobject. What is
the area of the slab, if it floats with its top surface just awash in fresh
water when a swimmer of mass m is on top?
Solution:
- Reasoning:
When an object floats, the magnitude of the buoyant force is equal to the
magnitude of its weight. The magnitude of the buoyant force is equal to the
magnitude of the weight wwater of the displaced water.
- Details of the calculation:
wwater
= ρwaterAhg, where A is the area of the slab.
The the magnitude of the weight of the object is wobject
= ρobjectAhg
+ mg.
We need wwater = wobject.
ρwaterAhg = ρobjectAhg + mg.
ρwaterAh - ρobjectAh = m.
A = m/(ρwaterh - ρobjecth).
Problem:
 A frog in a hemispherical pod finds that he just floats without sinking into
a sea of blue-green ooze with density 1.35 g/cm3. If the pod has
radius 6 cm and negligible mass, what is the mass of
the frog?
A frog in a hemispherical pod finds that he just floats without sinking into
a sea of blue-green ooze with density 1.35 g/cm3. If the pod has
radius 6 cm and negligible mass, what is the mass of
the frog?
Solution:
- Reasoning:
When an object floats, the magnitude of the buoyant force is equal to the
magnitude of its weight. The magnitude of the buoyant force is equal to the
magnitude of the weight wliquid of the displaced liquid.
- Details of the calculation:
wliquid
= ρliquidVg.
The volume V of the displaced liquid is the volume of one half sphere,
V = 2πr3/3 = 2π(6 cm)3/3 =
452 cm3.
The magnitude of the weight of the object is wobject
= mfrogg.
(We are neglecting the weight of the air-filled pod.)
ρliquidVg = mfrogg.
mfrog = 1.35 (g/cm3) 452 cm3 = 610 g.
Problem:
A barge is carrying a load of gravel along a river. It approaches a low
bridge, and the captain realizes that the top of the pile of gravel is not going
to make it under the bridge. The captain orders the crew to quickly shovel
gravel from the pile into the water. Is this a good decision?
Solution:
- Reasoning:
Assume an object has a weight w and a density ρ greater than that of water.
When the object floats in a boat, the weight of the water displaced because
of this object is equal to the weight of the object. When the object sinks
when thrown overboard, the weight of the displaced water is less than the
weight of the object. An object with ρ > ρwater of a given
weight displaces more water when floating than when being submerged. When a
given volume of gravel is shoveled into the water, a larger volume of the
ship will rise out of the water. But that does not necessarily mean that
the maximum height h of the load above the water's surface increases. This
maximum height h depends on how the load is distributed. If the load is
evenly spread over the entire deck of the ship, the shoveling sand into the
water is not a good idea. But if the load is a pyramid-shaped pile, then
removing the top of the pyramid is a good idea.
Problem:
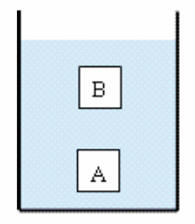 Two
objects, A and B, have the same volume and are completely submerged in a liquid,
although A is deeper than B. Which object, if either, experiences the greater
buoyant force?
Two
objects, A and B, have the same volume and are completely submerged in a liquid,
although A is deeper than B. Which object, if either, experiences the greater
buoyant force?
Solution:
- Reasoning:
The buoyant force B equal is equal in magnitude to the
weight w of the displaced liquid. Both objects displace the same amount of
liquid and therefore experience the same buoyant force.
(Even though the average pressure is higher at the position of A than at the
position of B, the difference between pressures on the top and on the bottom
of each block is the same. It is this pressure difference that is
responsible for the buoyancy.)
Watch this
short video clip!
External link:




 Consider again the box-shaped volume of
water in equilibrium at some depth in the pool. The upward force
provided by the surrounding water must exactly balance the force of
gravity acting on the water in the box. The upward force provided by
the surrounding water must be equal to the weight of water in the box.
Consider again the box-shaped volume of
water in equilibrium at some depth in the pool. The upward force
provided by the surrounding water must exactly balance the force of
gravity acting on the water in the box. The upward force provided by
the surrounding water must be equal to the weight of water in the box. A frog in a hemispherical pod finds that he just floats without sinking into
a sea of blue-green ooze with density 1.35 g/cm3. If the pod has
radius 6 cm and negligible mass, what is the mass of
the frog?
A frog in a hemispherical pod finds that he just floats without sinking into
a sea of blue-green ooze with density 1.35 g/cm3. If the pod has
radius 6 cm and negligible mass, what is the mass of
the frog?  Two
objects, A and B, have the same volume and are completely submerged in a liquid,
although A is deeper than B. Which object, if either, experiences the greater
buoyant force?
Two
objects, A and B, have the same volume and are completely submerged in a liquid,
although A is deeper than B. Which object, if either, experiences the greater
buoyant force?