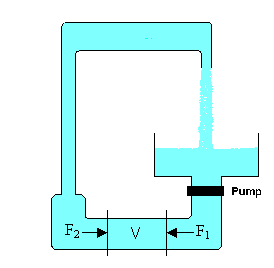
 Assume you have created an indoor water fountain.
You have connected pieces of pipe with different diameters into a path
along which the water will flow. You also have inserted a pump
into the circuit. A very simple circuit is shown in the figure on
the right.
Assume you have created an indoor water fountain.
You have connected pieces of pipe with different diameters into a path
along which the water will flow. You also have inserted a pump
into the circuit. A very simple circuit is shown in the figure on
the right.
Running the pump for a while will accelerate the water and start it flowing.
The pump creates a pressure gradient. If we
look at a volume V of water in a straight section of pipe while the water is
accelerating, then the pressure on side 1 of this volume is different than the
pressure on side 2. This results in a net force on the volume of water in that
section, and the volume of water accelerates.
Once the water is flowing at the chosen speed, the pump has to do much less
work. If the pressure were the same on both sides of the volume V, then the net
force would be zero, and the volume of water would continue to move with
constant velocity. However, there will still be a small pressure gradient due
to frictional forces. The pump now only has to do work against frictional
forces. Water is viscous, there is friction between its component
molecules as they slide past one another and past the walls of containers. In a frictionless environment
a pump would be no longer needed to keep the water flowing. Such a frictionless environment can actually be
created. While most liquids freeze at near zero absolute temperature, liquid
helium becomes a superfluid. It flows without friction. You do not need a pump
to keep a superfluid liquid Helium fountain operating.
External link:
Superfluid Helium (Youtube)
The equation of continuity
 Ideal fluids are incompressible and flow steadily without friction.
The flow is laminar and can be represented graphically by
streamlines.
In a straight section of pipe with constant cross sectional area all fluid
particles move with the same velocity. Different streamlines do not cross.
Ideal fluids are incompressible and flow steadily without friction.
The flow is laminar and can be represented graphically by
streamlines.
In a straight section of pipe with constant cross sectional area all fluid
particles move with the same velocity. Different streamlines do not cross.
 For simplicity let us assume a frictionless environment and let us assume
that water is an ideal fluid that flows steadily through a circuit.
The water in sections of
the circuit at different heights has different gravitational potential energy per unit volume.
In sections of the pipe with different cross-sectional areas the water
also must have different kinetic energy per unit volume. In the narrower
sections of the pipe it must flow faster than in the wider sections,
since the same amount of water must flow across each cross sectional
area in the same amount of time.
For simplicity let us assume a frictionless environment and let us assume
that water is an ideal fluid that flows steadily through a circuit.
The water in sections of
the circuit at different heights has different gravitational potential energy per unit volume.
In sections of the pipe with different cross-sectional areas the water
also must have different kinetic energy per unit volume. In the narrower
sections of the pipe it must flow faster than in the wider sections,
since the same amount of water must flow across each cross sectional
area in the same amount of time.
Look at a particular volume of water. As it moves, the boundary 1 moves a
distance l1 while boundary 2 moves a distance l2.
Since water is incompressible, we have
Volume 1 = Volume 2,
(Volume 1)/Δt = (Volume 2)/Δt.
The volume flow rate ΔV//Δt is the same everywhere. We now use Volume = area *length
for a cylinder.
(Area 1)*l1 = (Area 2)*l2
(Area 1)*Δl1/Δt = (Area 2)*Δl2/Δt
(Area 1)*v1 = (Area 2)*v2
This is the equation of continuity. The equation of continuity is a consequence of the
conservation of the mass of the water.
Problem:
The volume flow rate of water through a horizontal pipe is 2 m3/min.
Determine the speed of flow at a point where the diameter of the pipe is
(a) 10 cm,
(b) 5 cm.
Solution:
- Reasoning:
The equation of continuity, A*v = ΔV/Δt = constant, the volume
flow rate is the same everywhere.
The cross-sectional area A of the pipe is = πd2/4.
- Details of the calculation:
(πd2/4)v = (2 m3)/(60 s). v
= (0.042/d2) m/s with d measured in m.
(a) d = 10 cm:
v = 4.24 m/s
(b)
d = 5 cm: v = 16.98 m/s.
Bernoulli's equation
 In different sections of a pipe circuit, a volume V of water can have different potential
energy and different kinetic energy. Is the pressure also
different in different sections of the pipe circuit?
In different sections of a pipe circuit, a volume V of water can have different potential
energy and different kinetic energy. Is the pressure also
different in different sections of the pipe circuit?
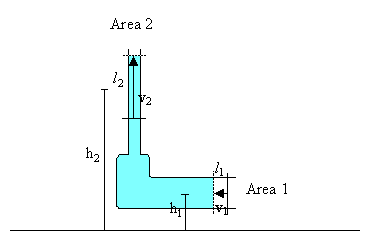
Refer to the figure on the right. The potential energy of the water changes as it moves. While
all the water moves, the change in potential energy is the same as that of a
volume V, which has been moved from position 1 to position 2 in the figure on
the right. The potential
energy of the water in the rest of the pipe is the same as the potential energy
of the water that used to be in the rest of the pipe before the movement. We have
change in potential energy = (mass of water in V)*g*(change in height)
= density*V*g*(h2 - h1) = ρVg(h2 - h1).
The kinetic energy of the water also changes. Again we only have to find the
change in kinetic energy in the small volume V, as if the water at position 1
had been replaced by the water at position 2. The kinetic energy of the water
in the rest of the pipe is the same as the kinetic energy of the water that used
to be in the rest of the pipe before the movement. We have
change in kinetic energy = ½mv22 - ½mv12
= ½ρVv22 - ½ρVv12.
If the force on the water at position 1 is different than the force on the
water at position 2, then work is done on the water as it moves.
Neglecting
friction, the amount of work done is W = F1l1 -
F2l2. But force = pressure times area, so
W = P1A1l1 - P2A2l2
= P1V - P2V .
The work must equal the change in energy. We therefore have
P1V - P2V = ρVg(h2-h1)
+ ½ρVv22 - ½ρVv12,
or
P1V + ρVgh1 + ½ρVv12 = P2V
+ ρVgh2 + ½ρVv22.
Dividing by V we have
P1 + ρgh1 + ½ρv12
= P2 + ρgh2 + ½ρv22
or
P + ρgh + ½ρv2 = constant.
This is Bernoulli's equation. It is a consequence of the
conservation of energy of the water.
 Assume you have created an indoor water fountain.
You have connected pieces of pipe with different diameters into a path
along which the water will flow. You also have inserted a pump
into the circuit. A very simple circuit is shown in the figure on
the right.
Assume you have created an indoor water fountain.
You have connected pieces of pipe with different diameters into a path
along which the water will flow. You also have inserted a pump
into the circuit. A very simple circuit is shown in the figure on
the right. Ideal fluids are incompressible and flow steadily without friction.
The flow is laminar and can be represented graphically by
streamlines.
In a straight section of pipe with constant cross sectional area all fluid
particles move with the same velocity. Different streamlines do not cross.
Ideal fluids are incompressible and flow steadily without friction.
The flow is laminar and can be represented graphically by
streamlines.
In a straight section of pipe with constant cross sectional area all fluid
particles move with the same velocity. Different streamlines do not cross. For simplicity let us assume a frictionless environment and let us assume
that water is an ideal fluid that flows steadily through a circuit.
The water in sections of
the circuit at different heights has different gravitational potential energy per unit volume.
In sections of the pipe with different cross-sectional areas the water
also must have different kinetic energy per unit volume. In the narrower
sections of the pipe it must flow faster than in the wider sections,
since the same amount of water must flow across each cross sectional
area in the same amount of time.
For simplicity let us assume a frictionless environment and let us assume
that water is an ideal fluid that flows steadily through a circuit.
The water in sections of
the circuit at different heights has different gravitational potential energy per unit volume.
In sections of the pipe with different cross-sectional areas the water
also must have different kinetic energy per unit volume. In the narrower
sections of the pipe it must flow faster than in the wider sections,
since the same amount of water must flow across each cross sectional
area in the same amount of time.