The building blocks of ordinary matter are atoms
and molecules. Molecules are two or more
atoms held together by a chemical bond. Atoms themselves are made up of more
fundamental particles, i.e. protons, neutrons, and electrons. In a
solid, the atoms and molecules are densely
packed and held in place by intermolecular forces. The atoms in a solid can be
modeled as being held together by tiny
springs that permit them to vibrate back and forth about their equilibrium
position, but not to exchange positions with other atoms. Solids are nearly
incompressible. In a
liquid the atoms and molecules are also densely packed. They
cannot easily escape from one another, but they are free to move with respect to
each other. Liquids are nearly incompressible. In a gas, intermolecular forces are weak and short ranged, and the atoms
and molecules can move about nearly independently. Gases are
compressible. Gases and liquids are
fluids, i.e. collections of atoms or
molecules that are free to move with respect to each other.
Density
Assume a substance in a volume V has mass M and is made up of N particles.
We define the particle density ρparticle
as the number of particles per unit volume, ρparticle = N/V.
We define the density ρ of the substance as
its mass per unit volume, ρ = M/V.
Problem:
A king orders a gold crown having a mass of 0.5 kg.
When it arrives from the metal smith, the volume of the crown is found to be 185
cm3. Is the crown made of solid gold? The density of gold is 1.9*103 kg/m3.
Solution:
- Reasoning:
Density ρ = M/V. M and V are given.
- Details of the calculation:
The density of the crown is (0.5 kg)/(185 cm3) * (106
cm3)/(1 m3) = 2.7*103 kg/m3.
The crown is not made of solid gold.
External link: Densities of
various materials
Pressure
We define the pressure P as the
magnitude of the normal force F exerted over an area A, divided by the area A.
Pressure equals force per unit area.
P = F/A
In SI units, the units of pressure
are N/m2 = Pa (pascal).
Examples:
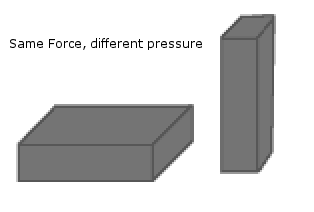 A brick is at rest on a table. The force with which
the brick pushes on the table is its weight, F = mg. The pressure it
exerts on the contact area depends on the brick's orientation. If
the contact area between brick and table is larger, the brick exerts
less pressure on the contact area.
A brick is at rest on a table. The force with which
the brick pushes on the table is its weight, F = mg. The pressure it
exerts on the contact area depends on the brick's orientation. If
the contact area between brick and table is larger, the brick exerts
less pressure on the contact area.
Grab a pencil with one hand and press the
flat end against your other hand. Press hard. Does it hurt?
Now turn the pencil around and press the tip of the pencil against
your other hand with the same force. Does it hurt now?

 A 50 kg woman balances on one heel of a high-heel shoe. If the heel is circular with
radius 0.5 cm, the pressure she exert on
the floor is
A 50 kg woman balances on one heel of a high-heel shoe. If the heel is circular with
radius 0.5 cm, the pressure she exert on
the floor is
P = F/A = (50 kg 9.8
m/s2)/(π(0.005 m)2) = 6.2*106 N/m2 = 6.2 MPa.
(1 MPa = 1000000 Pa)
If the woman wears a flat-heel shoe with a
radius of 3 cm then the pressure she exerts on the floor is
P
= F/A = (50 kg 9.8 m/s2)/(π(0.03 m)2) = 1.7*105N/m2 = 0.17 MPa.
The pressure she exerts is
reduced by a factor of 36. Be careful around women with high-heel shoes!
Hydrostatics
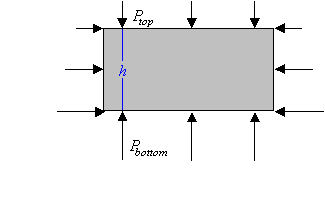
The pressure at a point below the surface of a liquid in
a constant gravitational field depends only on the depth of that point
and the pressure at the surface.
Any change in the pressure at the surface is therefore
transmitted to every point in the liquid.
This is called Pascal's law.
Consider a large pool of water on the surface of the earth and a box-shaped
volume of water at some depth in the pool. Imagine it enclosed by
some weightless container.
The volume of water is in equilibrium and stays in place. It does
not rise and it does not fall. The net force on it must be zero. The
vertical component of the net force is
Fnet = PbottomA - PtopA - Mg = 0.
Fnet = PbottomA - PtopA - ρhAg = 0.
Pbottom - Ptop = ρhg.
The pressure in the pool increases with depth. If we let h denote the vertical distance of a
point below the surface of the water, then we can write the pressure at this point as
Pbelow = Ptop + ρhg.
P is the pressure at depth h and P0 is the pressure at the
surface. Very often this pressure is atmospheric pressure. The
atmospheric pressure at sea level at
room temperature is approximately
1 atmosphere = 101 kPa = 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi).
Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. Gauge pressure is
positive for pressures above atmospheric pressure, and negative for pressures below it.
Absolute pressure
is the sum of gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure.
Problem:
Consider three drinking glasses. All three have the same area base, and all
three are filled to the same depth with water. Glass A is wider at the top than
at the bottom, glass B is cylindrical and so holds less water than A. Glass C is
narrower at the top than at the bottom, and so holds less water than B. Which
glass has the greatest liquid pressure at the bottom?
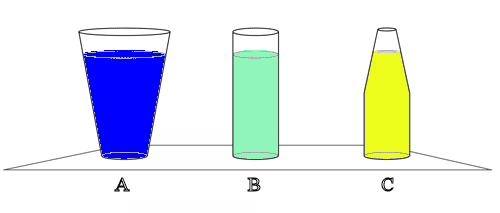
Solution:
- Reasoning:
The pressure at a point below the surface of a liquid in a constant
gravitational field depends only on the depth of that point and the pressure
at the surface. All three have equal pressure at the bottom
Watch this
short video clip!
Problem:
Determine the absolute pressure at the bottom of a lake that is 30 m
deep.
Solution:
- Reasoning:
The pressure at a point below the surface of a liquid in
a constant gravitational field depends only on the depth of that point
and the pressure at the surface.
P = P0 + ρgh. P0
= 101 kPa = 1 atm.
- Details of the calculation
ρwater
= 1000 kg/m3.
ρgh = 1000*9.8*30 N/m2 =
294 kPa ≈ 3 atm.
P ≈ 4 atm.
The water pressure increases by approximately 1 atm for every 10 m increase in depth.
Problem:
Intravenous infusions are usually made with the help of the gravitational force. Assume
that the density of the fluid being administered is very close to that
of water (1 g/cm3). At what height should the IV bag be placed
above the entry point so that the fluid just enters the vein if the
blood pressure in the vein is 18 torr = 2392 Pa above atmospheric
pressure? Assume that the IV bag is collapsible.
Solution:
- Reasoning:
For the fluid to enter the vein, its pressure at entry must just
exceed the blood pressure in the vein.
Pbelow = Ptop
+ ρhg, or
Patm + 2392 Pa = Patm + ρhg.
The gauge pressure ρhg must be just greater
than 2392 Pa.
- Details of the calculation:
Solving for h = (2392 Pa)/(ρg) = (2392 N/m2)/(1000
kg/m3 *9.8 m/s2) = 0.24 m = 24 cm.
The IV bag must be placed a little over 24 cm above the entry point for
the fluid to just enter the vein.
Problem:
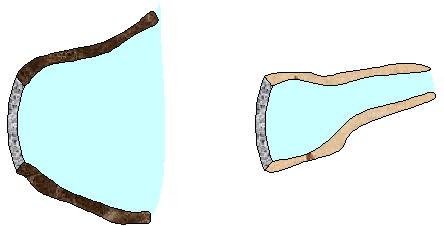 The figure on the right shows an aerial view from
directly above two dams. Both dams are equally long and equally deep.
The dam on the left holds back a very large lake and the dam on the
right holds back a narrow river. Which dam has to be build more
strongly?
The figure on the right shows an aerial view from
directly above two dams. Both dams are equally long and equally deep.
The dam on the left holds back a very large lake and the dam on the
right holds back a narrow river. Which dam has to be build more
strongly?
Solution:
- Reasoning:
The pressure at a point below the surface of a liquid in
a constant gravitational field depends only on the depth of that point
and the pressure at the surface.
The net force on both dams is the same, the strength of both dams
must be the same.
Problem:
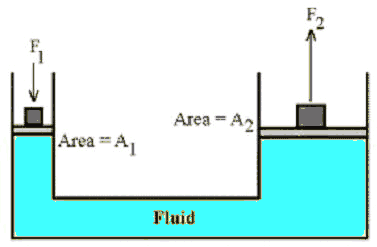 A hydraulic system is used to lift a 2000 kg vehicle in an auto garage. If
the vehicle sits on a piston of area 0.5 m2, and a force is
applied to a piston of area 0.03 m2, what is the minimum
force that must be applied to lift the vehicle?
A hydraulic system is used to lift a 2000 kg vehicle in an auto garage. If
the vehicle sits on a piston of area 0.5 m2, and a force is
applied to a piston of area 0.03 m2, what is the minimum
force that must be applied to lift the vehicle?
Solution:
- Reasoning:
Pascal's law:
When a force is applied to a contained, incompressible fluid, the
pressure increases by the same amount throughout the fluid.
This property of incompressible fluids can be used to amplify
forces, as is done in hydraulic lifts.
- Details of the calculation:
P1 = P2, F1/A1 = F2/A2,
F1 = (A1/A2)*F2 =
(0.03/0.5)*(2000 kg*9.8 m/s2) = 1180 N.
Conservation of energy requires that the work done on the system
must balance the work done by the system. In the hydraulic
lift the distance over which F1 is applied is be greater
than the distance over which F2 acts by the exact same
ratio as the force multiplier.
F1/F2 = d2/d1.
Embedded Question 1
Suppose the master cylinder in a hydraulic system is at a greater height than
the cylinder it is controlling. Explain how this will affect the force
produced at the cylinder that is being controlled.
Discuss this with your fellow students in the discussion forum!
 A brick is at rest on a table. The force with which
the brick pushes on the table is its weight, F = mg. The pressure it
exerts on the contact area depends on the brick's orientation. If
the contact area between brick and table is larger, the brick exerts
less pressure on the contact area.
A brick is at rest on a table. The force with which
the brick pushes on the table is its weight, F = mg. The pressure it
exerts on the contact area depends on the brick's orientation. If
the contact area between brick and table is larger, the brick exerts
less pressure on the contact area.
 A 50 kg woman balances on one heel of a high-heel shoe. If the heel is circular with
radius 0.5 cm, the pressure she exert on
the floor is
A 50 kg woman balances on one heel of a high-heel shoe. If the heel is circular with
radius 0.5 cm, the pressure she exert on
the floor is 

 The figure on the right shows an aerial view from
directly above two dams. Both dams are equally long and equally deep.
The dam on the left holds back a very large lake and the dam on the
right holds back a narrow river. Which dam has to be build more
strongly?
The figure on the right shows an aerial view from
directly above two dams. Both dams are equally long and equally deep.
The dam on the left holds back a very large lake and the dam on the
right holds back a narrow river. Which dam has to be build more
strongly? A hydraulic system is used to lift a 2000 kg vehicle in an auto garage. If
the vehicle sits on a piston of area 0.5 m2, and a force is
applied to a piston of area 0.03 m2, what is the minimum
force that must be applied to lift the vehicle?
A hydraulic system is used to lift a 2000 kg vehicle in an auto garage. If
the vehicle sits on a piston of area 0.5 m2, and a force is
applied to a piston of area 0.03 m2, what is the minimum
force that must be applied to lift the vehicle?